Triple bonds are not very common, as they require atoms to share so many electrons and to be very close to each other. Many elements are not even capable of forming a triple bond (for example hydrogen does not have enough electrons to create 3 separate bonds). The elements that can participate with triple bonds are:
- Nitrogen
- Carbon
- Boron
- Sometimes oxygen
These elements have enough electrons to form a triple bond and can form the sp hybridized electron orbital necessary to form the three bonds.
Nitrogen Triple Bond
Two compounds that utilize nitrogen and a triple bond are:
- Nitrogen gas: {eq}N_2 {/eq}
- Cyanide: {eq}HCN {/eq}
Nitrogen gas consists of two nitrogen atoms. Both have hybridized sp orbitals. These orbitals form one sigma bond and two pi bonds with each other.
 |
The nitrogen-nitrogen bond is extremely strong, and whenever it does break it releases so much energy that often explosions result.
In cyanide, or the cyanide ion (no hydrogen present, and a negative charge on the carbon), there is a triple bond between carbon and nitrogen. This triple bond makes cyanide very stable, and difficult to break apart. The negative charge on carbon allows it to form ionic bonds with cation compounds such as sodium to create sodium cyanide.
Acetylene Triple Bond
Acetylene is a compound with a triple bond between carbon and carbon. It has the formula of {eq}C_2H_2 {/eq}, where the two carbon atoms are triple bonded to each other and then each carbon has a single bond to a hydrogen atom.
 |
Notice that the structure ends up very straight and linear with no bends or curves between the atoms. The triple bond keeps the molecule straight and linear since there isn't much room for movement or for the molecule to bend.
Carbon Monoxide Triple Bond
Carbon monoxide is a compound with the chemical formula CO. Carbon and oxygen have a triple bond between them, sharing six electrons (three electron pairs). The oxygen ends up with a positive charge and the carbon ends up with a negative charge. Oxygen doesn't really like to have a positive charge, as it is highly electronegative. A positive charge means that it is slightly lower in electrons than it likes to be. This means that the oxygen holds very tightly onto the electrons it does have, in the form of the triple bond. This makes the triple bond between oxygen and carbon extremely strong. In fact, it is the strongest known bond.
 |
To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member.
Create your account
Triple bonds consist of three covalent bonds between two atoms, where each bond shares two electron pairs, making a total of six electrons being shared. A covalent bond is when two electrons (an electron pair) are shared between two atoms. This triple bond is extremely strong, creates a linear structure, and pulls the atoms close to each other creating a shorter bond. Examples of triple bonds are found in:
- Nitrogen gas
- Cyanide
- Acetylene
- Carbon monoxide
The triple bonds are formed with one sigma bond and two pi bonds, where the atoms have hybridized sp orbitals.
To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member.
Create your account
Video Transcript
Definition
Nitrogen gas makes up 78% of our atmosphere and is one of the strongest little molecules out there. This is because nitrogen gas is made up of two nitrogen atoms held together by a triple bond. A triple bond is formed when two atoms are sharing three pairs of electrons. Triple bonds between atoms are often represented by three parallel lines.
It is important to note that electrons are shared in pairs. Each shared pair of electrons is called a covalent bond. Two shared electrons equate to a single covalent bond. Three sets of two shared electrons equate to a triple covalent bond. Though there are only three distinct bonds in a triple bond, a total of six electrons are being shared.
Because six electrons are shared between two atoms, triple bonds are incredibly strong and require immense energy to break. Breaking a triple bond between two nitrogen atoms requires nearly six times the energy of breaking a single bond between two nitrogens. As well as being very strong, triple bonds are also very short. A triple bond between two carbons is approximately 25% shorter than a single bond between two carbons.
Triple Bonds and Electron Orbitals
Truly understanding triple bonds requires a closer look at what's going on with the crazy, unpredictable electrons that are involved.
Electrons buzz around an atom in particular shapes according to their energy level and distance from the nucleus. The organization of electrons around an atom is called the electron configuration, and the particular shapes inhabited by electrons are called electron orbitals. There are four shapes of electron orbitals, s, p, d and f. In triple bonds, the s and p orbitals are involved.
Each atom participating in the triple bond must shuffle electrons and orbitals around so that six electrons can be evenly shared. Each atom must first do some magic and fuse their outermost s orbital with a p orbital. This hybrid orbital is called sp and will contain two total electrons. As if it wasn't complicated enough, this bond is often referred to as a sigma bond. Each atom will then use the two remaining p orbitals to share electrons with the other atom. Electrons shared in p orbitals are called pi bonds.
A triple bond consists of one sigma bond and two pi bonds. The image shows how they are arranged between two nitrogen atoms. Together, the two dark green bands are one pi bond. The two light green bands are another pi bond. The orange band represents the sigma bond, made by overlapping sp orbitals.
 |
Examples
Many different compounds contain a triple bond. Here's a chart of some common compounds containing triple bonds.
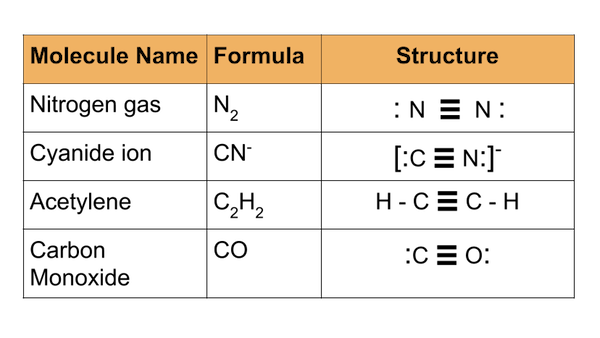
As noted earlier, nitrogen gas is 78% of our atmosphere, and also 78% of what we inhale and exhale every breath. The cyanide ion is notorious for its toxicity. If inhaled or ingested, this nasty compound inhibits essential cellular process, resulting in cell death.
Acetylene, a relatively unstable compound, is used as a fuel for cutting torches. Carbon monoxide is a rather infamous compound and rightly so. Carbon monoxide is essentially a poison; if inhaled, it fuses to blood cells, blocking their ability to carry oxygen. When blood cells cannot do their job and oxygenate the body, cells begin to die, and at worst, the organism will perish. Carbon monoxide is especially dangerous in that it has no odor and no color, so organisms have no warning when it is around.
Lesson Summary
A triple bond is formed when two atoms share three pairs of electrons. The sharing of two electrons is known as a covalent bond. Triple bonds are incredibly strong and rather short.
Triple bonds involve the sharing of electrons between two p orbitals of the bonding atoms, as well as the sharing of electrons between the sp orbital of each atom. When p orbitals are engaged in bonding, it is called a pi bond. When two sp orbitals are engaged in bonding, it is called a sigma bond. A triple bond is made of two pi bonds and one sigma bond. Examples of compounds with triple bonds include nitrogen gas, the cyanide ion, acetylene and carbon monoxide.
Learning Outcomes
Once you are finished with this lesson you should be able to:
- Provide the definition of a triple bond
- Explain the way in which triple bonds are formed
- Compare triple, pi and sigma bonds
- Name some common triple bonds
To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member.
Create your account